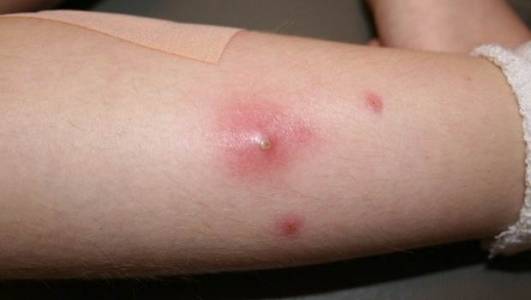
Staphylococcus, better known as Staph Infection, is a group of bacteria that can cause a number of diseases as a result a infections of tissues in the body. These infections can range from very mild cases to potentially fatal ones. Staph-related illnesses can come in over 30 different types but the most common is Staphylococcus aureus. This is normally found in the nose and on the skin of 25 to 30 percent of healthy adults. In most cases this will not cause any diseases by damage to the skin may allow the bacteria to overcome the natural protective mechanisms of the body and lead to infection. Staph infections can be detected with symptoms such as a impetigo (crusting of the skin), cellulitis or scalded skin. Breastfeeding women may also notice mastisis.
It is possible for anyone to contract a Staph infection but there are some groups of people who are more at risk than others. These include newborns, breastfeeding women and people with chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, vascular disease and lung disease. Drug users who inject, those with weaker immune systems, surgical incision or skin disorders may also be more at risk of developing a Staph infection. Until the infection has been resolved, Staph is contagious. The most common routes for the bacteria to spread are via contact with an infection wound by personal care items such as razors or bandages. There is not much of a risk of the infection spreading via casual contact such as hugging or kissing.
The name Staphylococcus comes from the Greek ‘staphyle’, meaning a bunch of grapes, and ‘kokkos’, which means berry. This name is derived from the fact that under the microscope, Staph bacteria look like a bunch of grapes or little berries. In technical terms this means that they are gram-positive, facultative anaerobic, usually encapsulated cocci.
It is possible for anyone to contract a Staph infection but there are some groups of people who are more at risk than others. These include newborns, breastfeeding women and people with chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, vascular disease and lung disease. Drug users who inject, those with weaker immune systems, surgical incision or skin disorders may also be more at risk of developing a Staph infection. Until the infection has been resolved, Staph is contagious. The most common routes for the bacteria to spread are via contact with an infection wound by personal care items such as razors or bandages. There is not much of a risk of the infection spreading via casual contact such as hugging or kissing.
The name Staphylococcus comes from the Greek ‘staphyle’, meaning a bunch of grapes, and ‘kokkos’, which means berry. This name is derived from the fact that under the microscope, Staph bacteria look like a bunch of grapes or little berries. In technical terms this means that they are gram-positive, facultative anaerobic, usually encapsulated cocci.